EN 14347:2005
Quantitative suspension test for the evaluation of basic sporicidal activity of chemical disinfectants and antiseptics.
EN 14347 is a phase 1 suspension test for the evaluation of basic sporicidal activity in chemical disinfectants. The result of a basic suspension test cannot be used to substantiate product claims and it is not valid for product registration. The test is applicable to active substances (antibacterial biocides) and to formulations under development that are planned to be used in food, industrial, domestic and institutional, medical and veterinary areas.
Test Conditions
The standard refers to the parameters to be observed when testing products intended for disinfection. This includes the test microorganism, test temperature, contact time and reference substances.
- Test microorganism refers to the mandatory list of microbes that must be used in the test to determine the antimicrobial activity of the product. The mandatory microorganisms are assumed to represent all microbes in its group.
- Test temperature refers to the temperature in which the test must be conducted. The general assumption is that disinfectants are less effective in low temperatures compared to higher temperatures.
- Contact time refers to the minimum duration a product must remain in contact with the microbes for the product to be effective.
One of the major differences between phase 1 basic suspension tests and phase 2 step 1 suspension tests is that phase 1 basic suspension tests do not include interfering substances in the test procedure.
Refer to the table below for the minimum and additional test conditions.

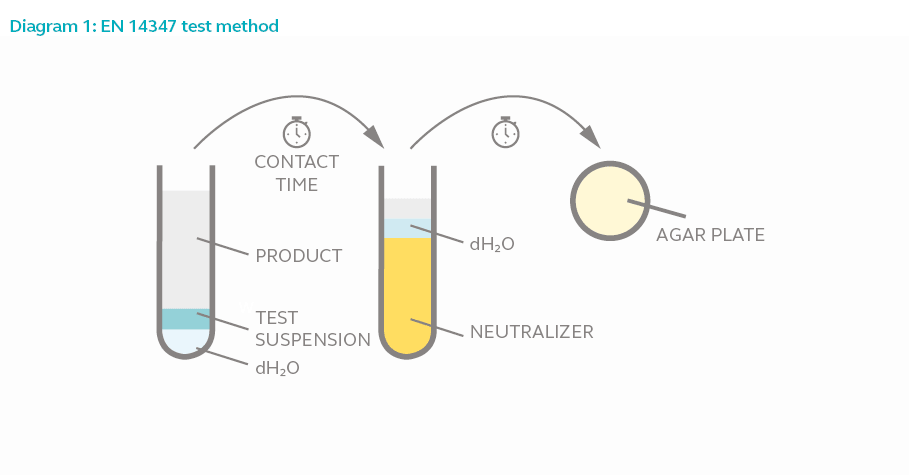
Test Method
In this phase 1 suspension test, 8 parts of test product is added to 1-part test microorganism and 1-part water. The mixture is allowed to interact for the duration of the contact time. 0.1 ml of the mixture is transferred to 10 ml TSB with neutralizer for 30 minutes to halt antimicrobial activity. Serial dilution is performed on the mixture, plated and incubated for 4-7 days to allow surviving spores (if any) to proliferate. The colony is counted and compared against the original culture size.
The test procedure also includes spore suspension susceptibility controls where the test is repeated with reference test solutions. Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus cereus spores are verified using two concentration levels of glutaraldehyde and peracetic acid solutions.
- With Bacillus subtilis without interfering substance:
- 3.0% (v/v) – 30 min: Glutaraldehyde solution should achieve a lg reduction of 1.55 ± 1.15 lg
- 0.05% (v/v) – 15 min: Peracetic acid solution should achieve a lg reduction of 2.4 ± 0.4 lg
- With Bacillus cereus without interfering substance:
- 1.0% (v/v) – 30 min: Glutaraldehyde solution should achieve a lg reduction of 3.45 ± 0.7 lg
- 0.1% (v/v) – 15 min: Peracetic acid solution should achieve a lg reduction of 1.25 ± 0.5 lg
Log Reduction
Log reduction refers to the extent to which a product is capable of reducing the number of microbes. For example, 4-log reduction means the number of microorganisms on a surface has been reduced by 10 000 times. A product that is 99.9% effective against a certain microbe is said to have achieved 3-log reduction against that microbe.
For a product to pass EN 14347, it must be able to achieve 4-log reduction against the respective test microorganisms listed in Table 1. In other words, the product must be able to kill 99.99% bacteria while meeting all the other requirements of the European standard.

